Our first week

According to the late French scholar, Agnes Cabrol, these 3 badly damaged sphinxes sitting east of Chapel D date stylistically to the reign of Ramesses III and probably had originally been part of a sphinx avenue leading north from that king’s temple at the southwest corner of the Isheru. We decided to test that theory this year.
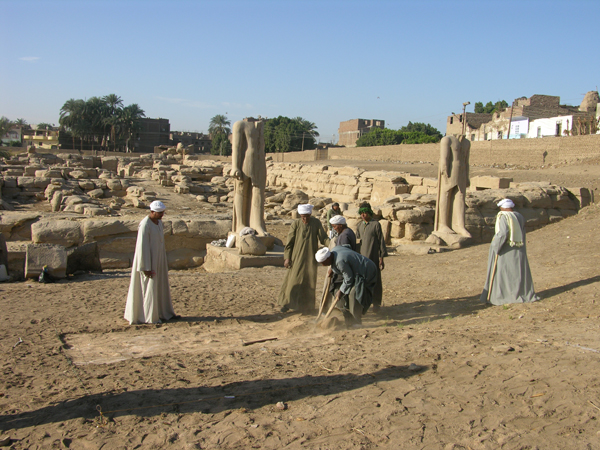

On Monday we opened a square north of the Ramesses III temple, where we hope to find remains of sphinx bases. Abdel Aziz is supervising the work.
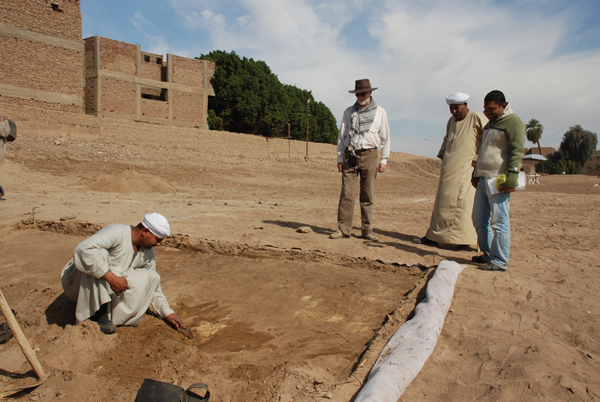

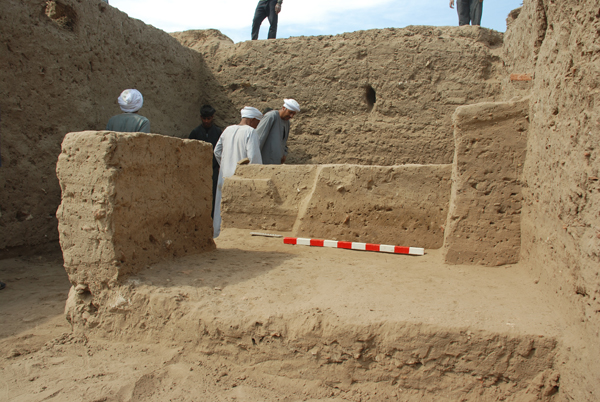
Jaap van Dijk, who arrived on Friday, discusses the new square with Farouk and Hassan. Welcome back, Jaap! As you can see, Abdel Aziz found sandstone almost immediately below the surface. The roll of white material you see on the right is the geo-textile laid down by the ARCE team to inhibit reed growth. When we have finished work here we will back-fill the excavation and put the material back in place.
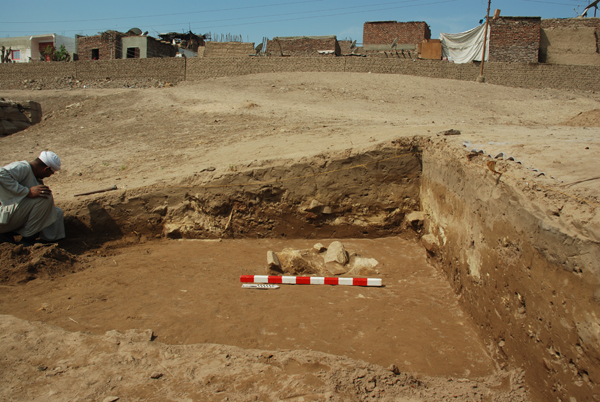

To our regret, Monday’s stone proved to be nothing but a shallow layer of badly decayed broken blocks, possibly dumped here by French archaeologist Maurice Pillet, who excavated the Ramesses III temple in the 1920s. Aside from one remaining cluster of stone, the square has produced nothing but clean dirt. If we don’t find anything of interest in a day or so, we’ll close this square and open another to its north.

Ayman is almost finished excavating his area west of the Taharqa Gate. All the gaps in the mud brick are the result of pitting. He should be down to the Dynasty 25 paving of the approach to the gate by Saturday. Once he finishes here, we’ll start another square further to the west to see if we can trace the paving further.

As part of the preparations to open the site to visitors, we will be helping the ARCE team relocate several blocks of temple decoration. This week we started building a new mastaba (Arabic for “bench”) on which to store the blocks. The mastabas are of baked brick with an impermeable layer between courses to prevent water infiltration. The final step is a finishing layer of cement. The work goes quickly with many willing hands.
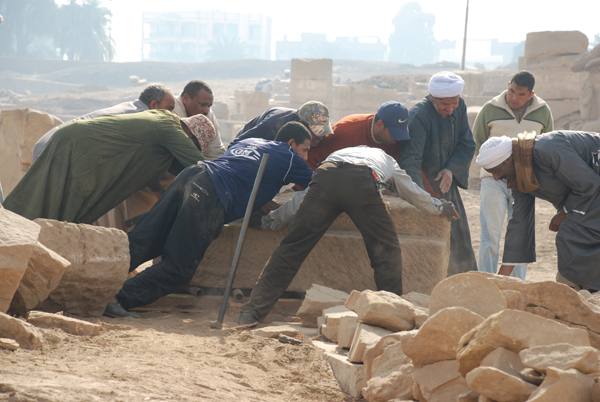

To build our second mastaba we had to move a large block several meters. Some stout beams, a few metal rollers and a lot of hard work and the task was accomplished.


We’re also clearing out an accumulation of broken stone just inside the precinct entrance. Since the stones are relatively small we use a sturdy cart that allows several to be moved at once. The work still requires a lot of effort, but more stones can be moved in fairly short order.
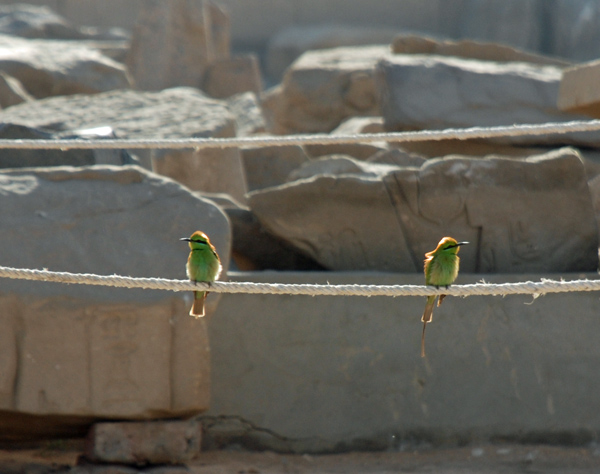

These brightly colored birds are a delight to watch as they snatch insects from the air. The underside of their wings is a coppery brown, so that when they fly you see flashes of green and copper.

Can you spot the bee-catcher? Despite its brilliant green plumage, this small bird (on the lower wire) can be very hard to make out against the foliage.

After a hard day’s work in the sun and dust, it is very restful to look out over the Nile at sunset.

Mary McKercher holds a BA in Ancient Near Eastern Studies (specializing in Egypt) from the University of Toronto and is also a trained archaeologist. In 1979 she joined the Brooklyn Museum’s expedition to the Precinct of the Goddess Mut at South Karnak as photographer and archaeologist, roles she continues to fill. She has contributed to the Mut Expedition’s “Dig Diary” since it began in 2005, and put together the photographs for the 8 Mut Expedition photo sets on the museum’s Flickr site. With her husband, Richard Fazzini, she has also researched and written about the West’s ongoing fascination with ancient Egypt, commonly known as Egyptomania.