Our last week of excavation
Our last day of excavation was February 28, but we still have work to do. Since we are leaving Luxor next week, this will be our last post from the field. We will do one last wrap-up posting on March 13 once we are back in Brooklyn.
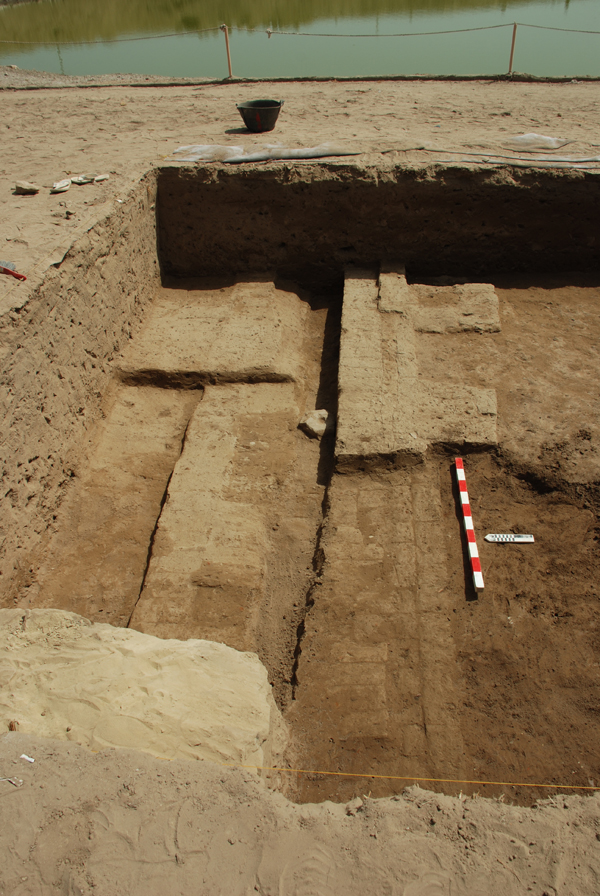

By mid week, Ayman was turning up some of the clearest and most beautifully laid bricks we have ever encountered. Even when first uncovered, two distinct parallel walls that occupy the full width of the square are clearly visible, with two shorter stubs of brick running off the southern wall. The block of stone between the rows is a door socket, but it seems to be displaced.
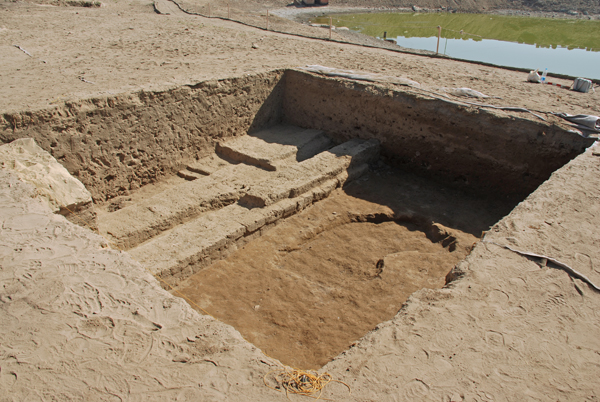

Ayman’s square at the end of the work, seen from the southwest. The two shorter walls were later additions built on dirt that had accumulated against the southern wall; they were removed. In the center of the square is a shallow, irregularly shaped pit that was filled with ash and pottery, mostly Ptolemaic. Unfortunately, we found no trace of sphinx bases.
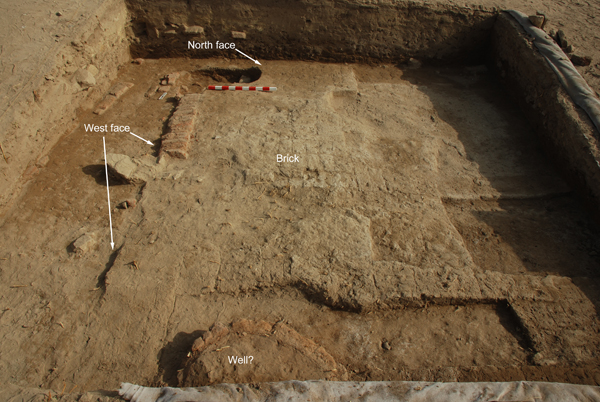

We extended Abdel Aziz’s square to the south to try to find the south face of the theoretical wall/pylon, and to the west to confirm that we do actually have the west face. The west face is real, but on the south the brick continued into the baulk, although it is broken by a later baked brick feature (a well?). The pottery associated with the well (?) is Ptolemaic.
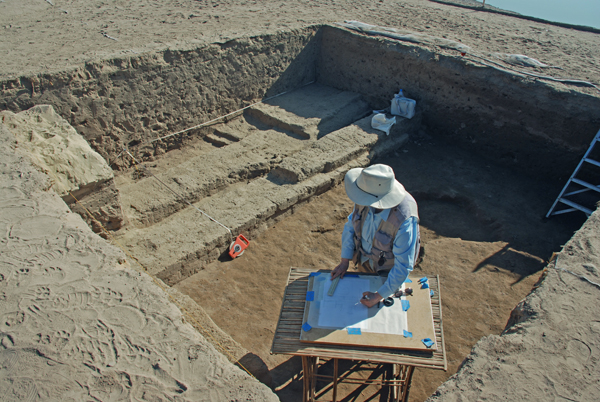

Before we back-filled the squares, they had to be mapped, and that is what I spent much of this week doing. It is very finicky work, particularly when dealing with mud brick. Since a heat wave hit Luxor this week, it was also very hot work.
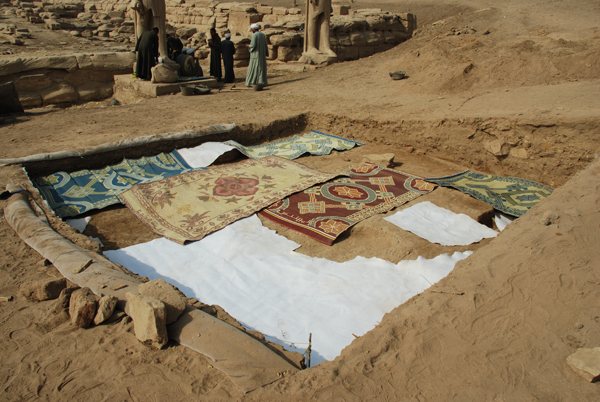

Once each square was mapped, we laid down plastic matting over the excavated surfaces then began back-filling the squares. Back-filling protects the features from erosion, and the plastic matting will let the next team to excavate here know when they have reached the limits of our work.


On Sunday the two blocks from the north face of Mut’s second pylon were put back into position, a delicate task as the blocks are different heights and neither has a flat lower surface. On the left, Jaap and the masons make sure the alignment is right as the eastern block is lowered into position. By the end of the week both blocks were in place and secure. All that remains now is to cover the new base with a coating tinted to blend in with the ancient stone.


We are building up the inner face of the enclosure wall west of the Propylon to keep brick debris from falling down onto the area below. The construction is of mud brick on top of baked brick, mimicking the ancient construction. On the left, the bricklayer studies the wall before he begins work as he will build it with the same batter as the face of the propylon. By mid-week he was almost finished (right).
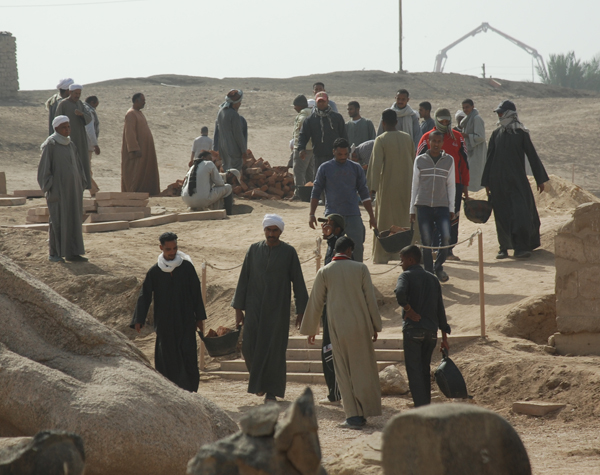

To get the bricks from the spot where they were delivered to the building sites, a procession of pairs of men carry baskets containing 3 or 4 bricks. This season’s work consumed over 4,000 baked bricks, which is a lot to move!
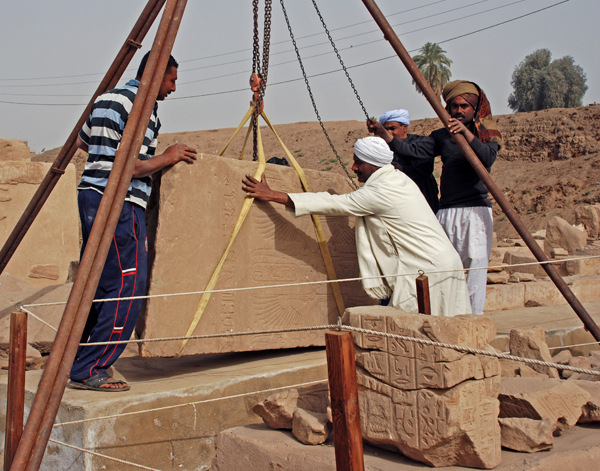

The first of the Chapel D ceiling blocks went up on its mastaba early in the week. While not as large as the huge block moved last week (the siba can handle it), it is still a sizable piece of stone that must be handled with care.

The ceiling blocks in their new home, with Chapel D behind them. The blocks on the mastaba in front of them are also from Chapel D.

By the end of work on Thursday we were almost finished building the mastabas. The ones that will hold the Taharqa ram (center) and a group of decorated blocks just inside the precinct entrance (right) received their finishing coats today. We will spend the rest of our time here getting the various sculptures, reliefs and decorated blocks onto their new bases. Preservation is an important component of any archaeological work.


I realized when I typed the last caption that you may not know what the “Taharqa ram” is or its significance. In 1979, at the north end of the Mut Temple’s East Porch we found the head of a ram with a king below its chin (left), along with fragments of the king’s body. The ram’s body was found nearby but had deteriorated to a shapeless mass of granite. Richard dated the head stylistically to the reign of Taharqa. In 2001, at the north end of the West Porch, we found the body (but not the head) of a second ram with the names of Taharqa on its base, thus confirming the dating of the head found in 1979. These two sculptures are among the very few rams of Taharqa found in Egypt. The ram’s head was taken to Cairo for the Museum of Egyptian Civilization.
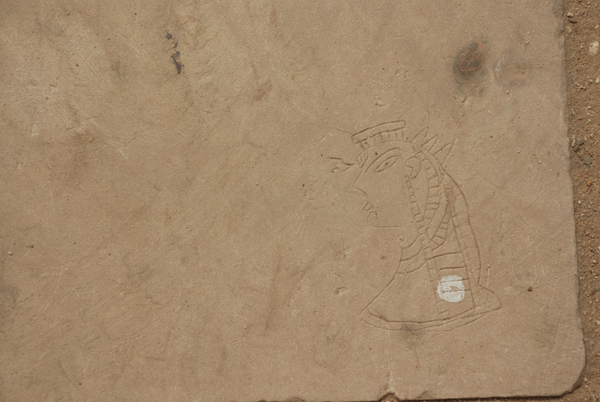

The new paving has acquired another graffito, probably by the same artist. This time he has chosen to show a queen or goddess, carved with the same skill as the first graffito.
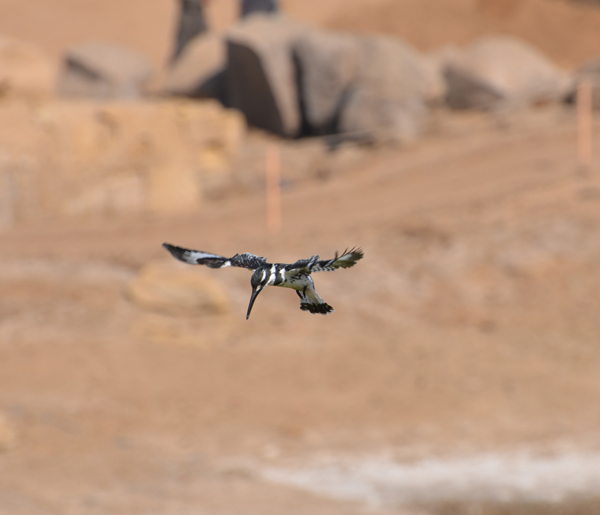

When she takes a break from pottery, Julia photographs the birds that feed in the sacred lake. She took this superb picture of a kingfisher poised to dive on Thursday.

Mary McKercher holds a BA in Ancient Near Eastern Studies (specializing in Egypt) from the University of Toronto and is also a trained archaeologist. In 1979 she joined the Brooklyn Museum’s expedition to the Precinct of the Goddess Mut at South Karnak as photographer and archaeologist, roles she continues to fill. She has contributed to the Mut Expedition’s “Dig Diary” since it began in 2005, and put together the photographs for the 8 Mut Expedition photo sets on the museum’s Flickr site. With her husband, Richard Fazzini, she has also researched and written about the West’s ongoing fascination with ancient Egypt, commonly known as Egyptomania.